Detection in immunohistochemistry is a crucial step that enables visualization of specific proteins within tissue samples. By translating the binding of antibodies to their target antigens into a visible signal, detection systems reveal the presence, localization, and distribution of proteins, which is fundamental for understanding biological processes and diagnosing diseases.
Chromogenic vs. Fluorescent Detection
There are two main categories of detection methods: chromogenic and fluorescent. Chromogenic detection relies on enzyme-conjugated antibodies that react with substrates to produce colored precipitates, visible under brightfield microscopy. This method is widely used due to its stability and ease of interpretation. Fluorescent detection uses fluorophore-labeled antibodies excited by specific wavelengths, enabling multiplexing and high sensitivity, though requiring specialized microscopy equipment.
Common Detection Methods
-
Direct Detection: Involves primary antibodies directly labeled with enzymes or fluorophores, allowing a simple one-step procedure but with limited sensitivity.
-
Indirect Detection: Uses unlabeled primary antibodies followed by enzyme- or fluorophore-labeled secondary antibodies, providing signal amplification and greater flexibility.
-
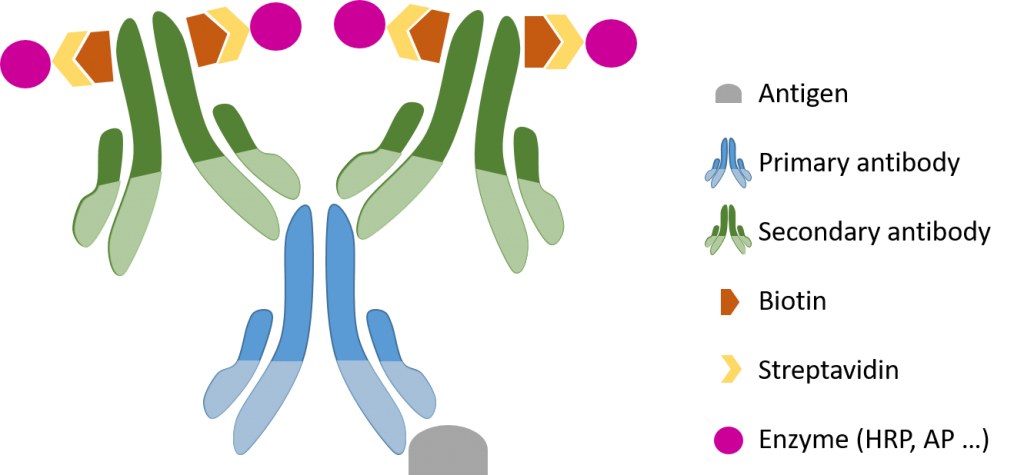
ABC (Avidin-Biotin Complex) Method: Amplifies signals using the strong affinity between avidin and biotin; widely used but sometimes affected by endogenous biotin.
-
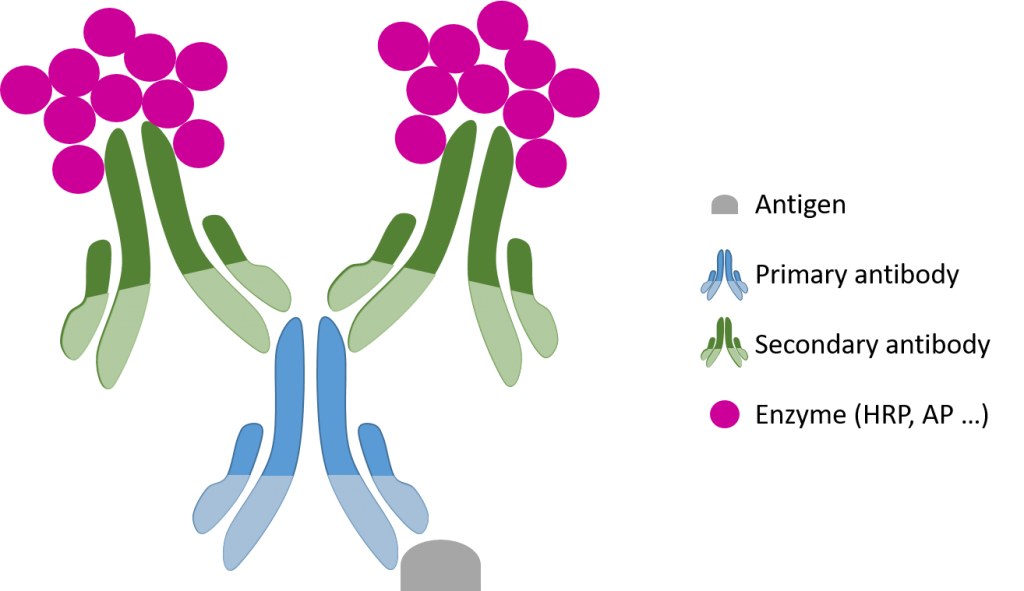
Polymer-Based Detection Kits: Utilize enzyme-labeled polymers attached to secondary antibodies, reducing background and simplifying workflows. These include specialized kits like Mouse on Mouse or Human on Human staining kits.
Advanced Techniques and Variants
Techniques such as tyramide signal amplification (TSA) provide high sensitivity by covalently depositing labeled tyramides at antigen sites. Multiplex fluorescent detection allows simultaneous visualization of multiple proteins. Other specialized methods include quantum dots and metallic labeling for specific applications.
Selecting the Appropriate Detection System
Choosing a detection system depends on factors including sample type, target protein, desired sensitivity, and available equipment. Proper selection and optimization are key to obtaining reliable, high-quality immunostaining result