KDEL Receptor Antibody
Katalog-Nummer OASE00041
Size : 100ug
Marke : Aviva Systems Biology
| Datasheets/Manuals | Printable datasheet for KDEL Receptor Antibody (OASE00041) |
|---|---|
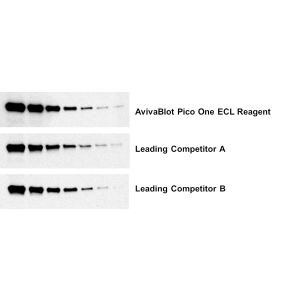
| COA Datasheet | 1 µg/ml was sufficient for detection of KDEL receptor in 20 µg monkey Vero cell lysate by colorimetric immunoblot analysis using Goat Anti-Mouse IgG:AP as the secondary. |
| Predicted Species Reactivity | Bovine|Chicken|Dog|Drosophila|Drosophila melanogaster|Hamster|Human|Monkey|Mouse|Porcine|Rabbit|Rat|Sheep|Xenopus|Xenopus laevis |
|---|---|
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone | KR-10 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Host | Mouse |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Application | ICC,IF,IHC,IP,WB |
| Additional Information | Background Info: Detects an ~25kDa protein corresponding to the molecular mass of KDEL on SDS-PAGE immunoblots. |
| :: | Scientific Background: The endoplasmic reticulum is part of a protein sorting pathway, or in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell. The majority of endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum through a retention motif. This motif is composed of four amino acids at the C-terminal end of the protein sequence. The most common retention sequence is KDEL (lys-asp-glu-leu). However, variation on KDEL does occur and other sequences can also give rise to endoplasmic reticulum retention (6). There are three KDEL receptors in mammalian cells, all have a very high degree of sequence identity; and all are located within the cis-Golgi and its intermediate compartments (4). In terms of function, KDEL receptors interact with GAP (GTPase-activating protein) of ARF1, which is involved in COPI dependent vesicle transport, and the KDEL receptor may also be responsible for the recruitment of this ARF1 to membranes which can then aid in the regulation of vesicle budding (3). It is also important to note that the KDEL receptor exhibits extensive sequence identity o yeast protein Erd2p, which is a receptor for the yeast ER retention signal (4, 5). |
| :: | Certificate of Analysis: 1ug/ml was sufficient for detection of KDEL receptor in 20ug monkey Vero cell lysate by colorimetric immunoblot analysis using Goat Anti-Mouse IgG:AP as the secondary. |
| Reconstitution and Storage | -20°C |
| Immunogen | A 21 residue synthetic peptide (amino acids 192-212) based on the bovine KDEL receptor and the peptide coupled to KLH |
| Purification | Protein G Purified |
| Concentration | 1 mg/ml |
| Specificity | Detects ~25kDa. |
| Dilution | WB (1:1000), ICC/IF (1:1000); optimal dilutions for assays should be determined by the user. |
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH7.2, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide |
| Description | The endoplasmic reticulum is part of a protein sorting pathway, or in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell. The majority of endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum through a retention motif. This motif is composed of four amino acids at the C-terminal end of the protein sequence. The most common retention sequence is KDEL (lys-asp-glu-leu). However, variation on KDEL does occur and other sequences can also give rise to endoplasmic reticulum retention (6). There are three KDEL receptors in mammalian cells, all have a very high degree of sequence identity; and all are located within the cis-Golgi and its intermediate compartments (4). In terms of function, KDEL receptors interact with GAP (GTPase-activating protein) of ARF1, which is involved in COPI dependent vesicle transport, and the KDEL receptor may also be responsible for the recruitment of this ARF1 to membranes which can then aid in the regulation of vesicle budding (3). It is also important to note that the KDEL receptor exhibits extensive sequence identity o yeast protein Erd2p, which is a receptor for the yeast ER retention signal (4, 5). |
| Reference | 1. Whiteman P., and Handford P.A. (2003) Hum Mol Genet 12(7): 727-737. 2. Forthoffer N., et al. (2002) J Bioenerg Biomemb 34(3): 209-219. 3. Aoe T., et al. (1997) EMBO J. 16: 7305-7316. 4. Tang B.L., Wong S.H, Qi X.L. Low S.H., and Hong W. (1993) J. Cell Biol. 120: 325-328. 5. Lewis M.J. and Pelham H.R. (1990) Nature 348: 162-163. 6. Spurger L. (2002). Endoplasmic reticulum: Structure and function. University of Texas Medical Branch. Retrieved September 13, 2006, from http://cellbio.utmb.edu/cellbio/rer1.htm |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | KDELR1 |
| Gene Full Name | KDEL endoplasmic reticulum protein retention receptor 1 |
| Alias Symbols | ER lumen protein-retaining receptor 1, KDEL (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) endoplasmic reticulum protein retention receptor 1, KDEL endoplasmic reticulum protein retention receptor 1, KDEL receptor 1. |
| NCBI Gene Id | 618184 |
| Protein Name | ER lumen protein-retaining receptor 1|ER lumen protein-retaining receptor 1 [Bos taurus] |
| Description of Target | Required for the retention of luminal endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins via vesicular recycling. This receptor recognizes the C-terminal K-D-E-L motif. COPI-coated transport intermediates, either in the form of round vesicles or as tubular processes, mediate retrograde traffic of the KDEL receptor-ligand complexes. Also required for normal vesicular traffic through the Golgi (By similarity). |
| Uniprot ID | P33946 |
| Protein Accession # | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001069963.1 |