Biotrend > CD59 Antibody
CD59 Antibody
Katalog-Nummer OAEE00929
Size : 100tests(T100)
Marke : Aviva Systems Biology
Weitere Informationen anfordern
Bitte melden Sie sich an, um diese Funktion zu nutzen.
| Datasheets/Manuals | Printable datasheet for CD59 Antibody |
|---|
| Predicted Species Reactivity | Human |
|---|---|
| Product Format | Stabilizing phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 15 mM sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone | MEM-43 |
| Isotype | IgG2a |
| Host | Mouse |
| Conjugation | APC |
| Application | FC |
| Reconstitution and Storage | 2°C to 8°C |
| Immunogen | Thymocytes and T lymphocytes |
| Purification | Purified by size-exclusion chromatography |
| Concentration | 10 ul / test |
| Specificity | The antibody MEM-43 reacts with well defined epitope (W40, R-53) on CD59 (Protectin), an 18-20 kDa glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored glycoprotein expressed on all hematopoietic cells; it is widely present on cells in all tissues. HLDA IV; WS Code NL 705 HLDA V; WS Code AS S013 HLDA V; WS Code BP BP345 HLDA V; WS Code T T-103 |
| Formulation | APC |
| Storage Buffer | The reagent is provided in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 15 mM sodium azide and 0.2% (w/v) high-grade protease free Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a stabilizing agent. |
| Reference | Robert Sutherland D, Keeney M, Illingworth A: Practical guidelines for the high-sensitivity detection and monitoring of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) clones by flow cytometry. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2012 Apr 12. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21023. [Epub ahead of print]Note: This article recommends PE-conjugated MEM-43 as a good reagent for red blood cell analysis of PNH (Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria) by flow cytometry. Stefanova I, Hilgert I, Kristofova H, Brown R, Low MG, Horejsi V: Characterization of a broadly expressed human leucocyte surface antigen MEM-43 anchored in membrane through phosphatidylinositol. Mol Immunol. 1989 Feb;26(2):153-61. Stefanova I, Horejsi V, Ansotegui IJ, Knapp W, Stockinger H: GPI-anchored cell-surface molecules complexed to protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1016-9. Cinek T, Horejsi V: The nature of large noncovalent complexes containing glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane glycoproteins and protein tyrosine kinases.J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2262-70. Bodian DL, Davis SJ, Morgan BP, Rushmere NK: Mutational analysis of the active site and antibody epitopes of the complement-inhibitory glycoprotein, CD59. J Exp Med. 1997 Feb 3;185(3):507-16., Cebecauer M, Cerny J, Horejsi V: Incorporation of leucocyte GPI-anchored proteins and protein tyrosine kinases into lipid-rich membrane domains of COS-7 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Feb 24;243(3):706-10. Forsberg UH, Bazil V, Stefanova I, Schroder J: Gene for human CD59 (likely Ly-6 homologue) is located on the short arm of chromosome 11. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(3):188-93. Horejsi V, Hilgert I, Kristofova H, Bazil V, Bukovsky A, Kulhankova J: Monoclonal antibodies against human leucocyte antigens. I. Antibodies against beta-2-microglobulin, immunoglobulin kappa light chains, HLA-DR-like antigens, T8 antigen, T1 antigen, a monocyte antigen, and a pan-leucocyte antigen. Folia Biol (Praha). 1986;32(1):12-25. (original description of MEM-43 antigen) Ilangumaran S, Briol A, Hoessli DC: CD44 selectively associates with active Src family protein tyrosine kinases Lckand Fyn in glycosphingolipid-rich plasma membrane domains of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Blood. 1998 May 15;91(10):3901-8. Omidvar N, Wang EC, Brennan P, Longhi MP, Smith RA, Morgan BP: Expression of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored CD59 on target cells enhanceshuman NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 2006 Mar 1;176(5):2915-23. And many other. Leukocyte Typing V., Schlossman S. et al. (Eds.), Oxford University Press (1995). Leukocyte Typing IV., Knapp W. et al. (Eds.), Oxford University Press (1989). Baalasubramanian S, Harris CL, Donev RM, Mizuno M, Omidvar N, Song WC, Morgan BP: CD59a is the primary regulator of membrane attack complex assembly in the mouse. J Immunol. 2004 Sep 15;173(6):3684-92. Menu E, Tsai BC, Bothwell AL, Sims PJ, Bierer BE: CD59 costimulation of T cell activation. CD58 dependence and requirement for glycosylation. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2444-56. Rooney IA, Davies A, Griffiths D, Williams JD, Davies M, Meri S, Lachmann PJ, Morgan BP: The complement-inhibiting protein, protectin (CD59 antigen), is present and functionally active on glomerular epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):251-6. Meri S, Morgan BP, Davies A, Daniels RH, Olavesen MG, Waldmann H, Lachmann PJ: Human protectin (CD59), an 18,000-20,000 MW complement lysis restricting factor,inhibits C5b-8 catalysed insertion of C9 into lipid bilayers. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):1-9. |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | CD59 |
| Gene Full Name | CD59 molecule (CD59 blood group) |
| Alias Symbols | 16.3A5, 1F5, 1F5 antigen, 20 kDa homologous restriction factor, CD59 antigen p18-20 (antigen identified by monoclonal antibodies 16.3A5, EJ16, EJ30, EL32 and G344), CD59 blood group antigen, CD59 glycoprotein, CD59 molecule, complement regulatory protein, EJ16, EJ30, EL32, G344, HRF-20, HRF20, human leukocyte antigen MIC11, Ly-6-like protein, lymphocytic antigen CD59/MEM43, MAC-inhibitory protein, MAC-IP, MACIF, MEM43, MEM43 antigen, membrane attack complex (MAC) inhibition factor, membrane attack complex inhibition factor, membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis, MIC11, MIN1, MIN2, MIN3, MIRL, MSK21, p18-20, protectin, surface anitgen recognized by monoclonal antibody 16.3A5, T cell-activating protein. |
| NCBI Gene Id | 966 |
| Protein Name | CD59 glycoprotein |
| Description of Target | Potent inhibitor of the complement membrane attack complex (MAC) action. Acts by binding to the C8 and/or C9 complements of the assembling MAC, thereby preventing incorporation of the multiple copies of C9 required for complete formation of the osmolytic pore. This inhibitor appears to be species-specific. Involved in signal transduction for T-cell activation complexed to a protein tyrosine kinase. |
| Uniprot ID | P13987 |
| Protein Accession # | NP_000602.1; NP_001120695.1; NP_001120697.1; NP_001120698.1; NP_001120699.1; NP_976074.1; NP_976075.1; NP_976076.1 |
| Nucleotide Accession # | NM_000611.5; NM_001127223.1; NM_001127225.1; NM_001127226.1; NM_001127227.1; NM_203329.2; NM_203330.2; NM_203331.2 |
Protein interactions
| Name | # of Products |
|---|---|
| C8A | 25 |
| C9 | 28 |
| CD2 | 157 |
| CD8A | 170 |
| CD9 | 120 |
| Gag | 136 |
| GNAI3 | 102 |
| NCR1 | 35 |
| NCR3 | 29 |
| SLC6A8 | 19 |
| SMAD4 | 396 |
| SRC | 773 |
| Vif | 72 |
Biological pathways
| Name | # of Products |
|---|---|
| Blood coagulation | 747 |
| Cell surface receptor linked signaling pathway | 420 |
Biological process
| Name | # of Products |
|---|---|
| Blood coagulation | 396 |
| Cell surface receptor signaling pathway | 179 |
Cellular components
| Name | # of Products |
|---|---|
| Anchored to external side of plasma membrane | 12 |
| Anchored to membrane | 100 |
| Cell surface | 369 |
| Extracellular region | 1573 |
| Membrane fraction | 437 |
| Plasma membrane | 2678 |
Protein function
| Name | # of Products |
|---|---|
| Protein binding | 12191 |
-
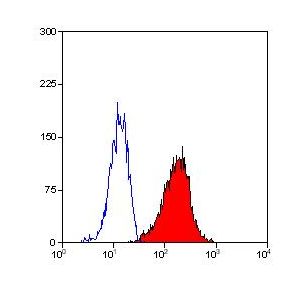 CD59 Antibody (OASA02286)Catalog #: OASA02286Clone: MEM-43Application: ELISA|EM|FC|IEM|IF|IHC-Fr|IHC-P|IP|WBFormat: Liquid. Phosphate buffered salineSize: 100UG
CD59 Antibody (OASA02286)Catalog #: OASA02286Clone: MEM-43Application: ELISA|EM|FC|IEM|IF|IHC-Fr|IHC-P|IP|WBFormat: Liquid. Phosphate buffered salineSize: 100UG -
 CD59 Antibody - FITC Conjugated (OACA00259)Catalog #: OACA00259Conjugation: FITCApplication: WBFormat: LiquidSize: 100ug
CD59 Antibody - FITC Conjugated (OACA00259)Catalog #: OACA00259Conjugation: FITCApplication: WBFormat: LiquidSize: 100ug -
 CD59 Antibody - Biotin Conjugated (OACA00260)Catalog #: OACA00260Conjugation: BiotinApplication: ELISAFormat: LiquidSize: 100ug
CD59 Antibody - Biotin Conjugated (OACA00260)Catalog #: OACA00260Conjugation: BiotinApplication: ELISAFormat: LiquidSize: 100ug -
 CD59 AntibodyCatalog #: OAEE00930Conjugation: FITCClone: MEM-43Application: FCFormat: Stabilizing phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 15 mM sodium azideSize: 100T
CD59 AntibodyCatalog #: OAEE00930Conjugation: FITCClone: MEM-43Application: FCFormat: Stabilizing phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 15 mM sodium azideSize: 100T -
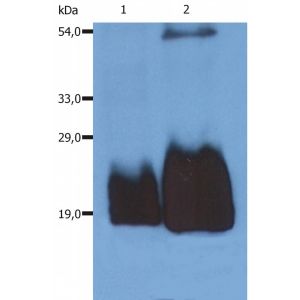 CD59 AntibodyCatalog #: OAEE00287Clone: MEM-43/5Application: FC|IHC-P|IP|WBFormat: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 15 mM sodium azideSize: 100UG
CD59 AntibodyCatalog #: OAEE00287Clone: MEM-43/5Application: FC|IHC-P|IP|WBFormat: Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, 15 mM sodium azideSize: 100UG



